Freight brokers play a crucial role in the transportation industry, acting as intermediaries between shippers and carriers. One of the most critical aspects of operating a successful freight brokerage is ensuring proper insurance coverage. Understanding freight broker insurance requirements and the various costs associated with obtaining coverage is essential for new and established brokers.
What is Cargo Insurance?
Cargo insurance is a policy that covers physical loss or damage to freight while in transit. It protects shippers, carriers, and brokers from financial losses due to theft, accidents, or natural disasters. Freight broker cargo insurance ensures that shipments are safeguarded against unforeseen risks, providing peace of mind to all parties involved in the logistics process.
Cargo theft costs the trucking industry over $30 billion annually (ATRI, n.d.). Having the right cargo insurance is essential for mitigating these losses.
“Cargo insurance isn’t just a compliance checkbox—it’s a risk management tool. To determine adequate coverage limits, brokers should assess their clients’ shipment values and frequency.”
What is Contingent Cargo Insurance?
Contingent cargo insurance for freight brokers is a secondary coverage that occurs when a carrier’s primary cargo insurance fails to cover a claim. This policy ensures that freight brokers are not left financially responsible for damaged or lost goods due to the carrier’s insurance coverage gaps. The contingent cargo insurance cost varies based on coverage limits, claim history, and business size.
For example, in 2023, a Florida-based freight brokerage faced a $500,000 cargo claim due to an uninsured carrier’s involvement. Their contingent cargo insurance covered the loss, preventing financial ruin (FreightWaves, 2023).
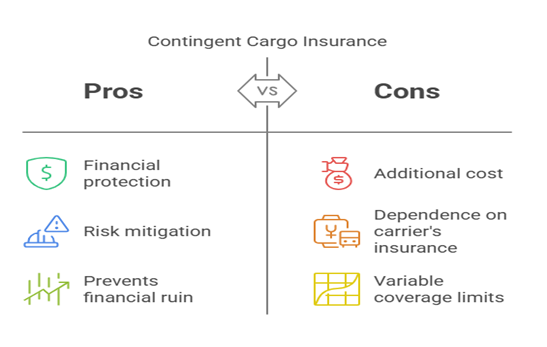
“Contingent coverage is critical because carrier policies often have exclusions (e.g., improper loading, perishable goods). Brokers should verify carriers’ insurance certificates annually and ensure their contingent policy matches their typical shipment values.”
How do you think contingent cargo insurance can help brokers build with their clients? Can brokers rely solely on contingent coverage, or should they also focus on ensuring their own primary coverage?
The Difference between Freight Insurance and Cargo Insurance
Many brokers and shippers often confuse freight insurance with cargo insurance. Here are the key differences:
- Freight Insurance: Protects the freight broker or carrier against liability claims related to damaged or lost goods during transportation.
- Cargo Insurance specifically covers physical cargo, reimbursing the shipper or consignee for financial losses incurred due to damage or loss of goods in transit.
Understanding these distinctions helps brokers choose the right policies, such as freight brokerage insurance and freight broker contingent cargo insurance to ensure complete protection.
“Misunderstanding these terms can lead to coverage gaps. Freight insurance shields your business; cargo insurance protects your clients. Always clarify which party is responsible for purchasing cargo coverage in contracts—this avoids disputes when claims arise.”
In your opinion, how can brokers effectively communicate the differences between freight insurance and cargo insurance to their clients? Do you think this is an area where many brokers make mistakes, leading to potential misunderstandings?
Why Cargo Insurance Matters for Freight Brokers
Cargo insurance protects freight brokers from financial losses from damaged, lost, or stolen goods. Without proper coverage, brokers could be liable for claims that could severely impact their business. The right contingent cargo insurance for freight brokers provides protection when a carrier’s primary insurance fails to cover a claim. Choosing the best contingent cargo insurance for freight brokers can safeguard against unforeseen risks and financial instability.
“Without sufficient insurance, brokers are exposed to significant financial and reputational risk. Cargo insurance isn’t optional in today’s freight brokerage environment—mitigating unexpected losses is necessary.”
What strategies can freight brokers employ to assess and mitigate the risks associated with cargo theft or damage?
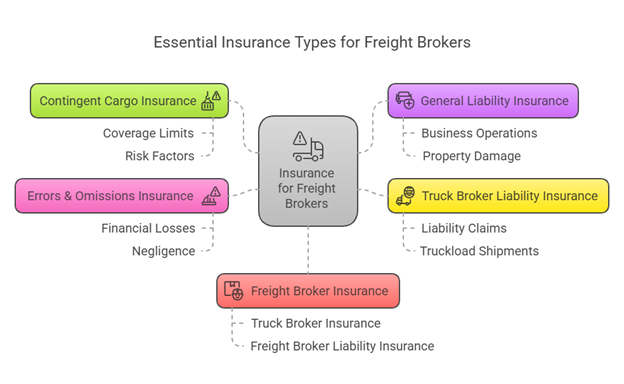
Key Types of Insurance for Freight Brokers
A freight broker course free of charge can be a great way to gain structured knowledge. Some training providers offer freight broker agent training online, with free introductory courses that cover the basics, allowing you. There are several insurance types that freight brokers should consider:
- Contingent Cargo Insurance: This policy is a backup when a carrier’s cargo insurance fails to pay for a loss. The cost of contingent cargo insurance varies based on coverage limits and risk factors.
Example: A brokerage specializing in high-value electronics found contingent cargo insurance helped cover a $300,000 loss when a carrier’s policy excluded theft coverage.
- General Liability Insurance: This covers bodily injury and property damage that may arise during business operations.
Example: A freight brokerage office had a visitor slip and fall, resulting in a $50,000 medical claim that was covered by their general liability policy
- Truck Broker Liability Insurance: This is specifically tailored to protect brokers from liability claims related to truckload shipments.
Example: A broker arranged a shipment in which a carrier improperly secured the load, causing an accident. The liability insurance covered the resulting legal and damage claims, amounting to $200,000.
- Freight Broker Contingent Cargo Insurance: A specialized policy that provides an additional safety net when carrier insurance does not respond adequately to a claim.
Example: A broker faced a claim when a carrier’s insurance denied coverage due to improper documentation. Their contingent cargo insurance covered the $150,000 claim, ensuring smooth operations.
- Errors & Omissions Insurance: Protects brokers from mistakes or negligence that may result in financial losses for shippers.
Example: A freight broker mistakenly provided incorrect shipping details, leading to delays and financial losses for a client. Their E&O insurance covered the $75,000 claim.
- Freight Broker Insurance: Comprehensive coverage that includes truck broker insurance and freight broker liability insurance to ensure compliance and financial security.
Example: A freight broker suffered a cyberattack that compromised sensitive shipment data. Their comprehensive insurance helped recover $100,000 in financial losses and legal costs.
According to the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), freight brokers must maintain a $75,000 surety bond or trust fund. However, additional insurance is highly recommended to cover unforeseen losses (FMCSA, n.d.).
“Each type of insurance plays a specific role in safeguarding your business. Assessing risks in your operations will help determine the best combination of coverage for long-term stability.”
Looking for tailored solutions for freight brokers? Reach out to explore how we can help.
Factors Affecting the Cost of Freight Broker Insurance
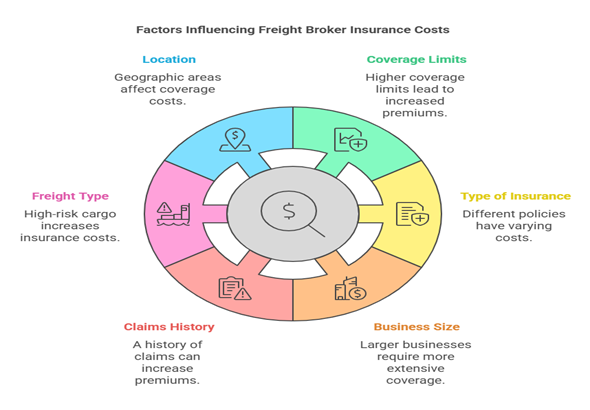
The freight broker insurance cost depends on several factors, including:
Location and Operating Regions: Coverage costs vary based on geographic areas and risk levels.
Coverage Limits: Higher limits lead to higher premiums.
Type of Insurance: Different policies, such as freight broker insurance or contingent cargo insurance, have varying costs.
Business Size: Larger freight brokerages typically require more extensive coverage.
Claims History: A history of claims can increase premiums.
Freight Type: High-risk cargo, such as hazardous materials, increases insurance costs.
“The cost of insurance for freight brokers is influenced by a combination of internal and external factors. Brokers should take a proactive approach to risk management by evaluating their operational needs and claims history regularly”
Which of the factors listed in this section do you think is most impactful in determining insurance premiums for freight brokers, and why?
How Much Does It Cost to Become a Freight Broker?
Many aspiring brokers ask, how much does it cost to become a freight broker? The cost can vary depending on licensing fees, insurance, and initial setup expenses. Below is a breakdown of typical expenses:
- Freight Broker License Cost: The FMCSA requires a $300 application fee to obtain a freight broker license (FMCSA, n.d.).
- Broker Authority Cost: The cost of obtaining operating authority (MC Number) is around $300.
- Truck Broker License Cost: The freight broker authority cost is essentially the same.
- Freight Broker Insurance Cost: Insurance costs depend on coverage limits and company size but can range from $1,000 to $10,000 annually.
- Freight Broker Startup Cost: In addition to insurance and licensing, brokers must consider office setup, software, and marketing, which can add up to $5,000–$10,000.
- Freight Broker Training Cost: Freight broker training costs range from $500 to $3,000 depending on the program.
- Broker License for Trucking: The total cost, including all fees and insurance, can range from $5,000 to $15,000.
“Starting as a freight broker is an investment, and it’s important to budget for both licensing and insurance. These upfront costs ensure you’re covered and compliant when operations begin.”
Explore how technology can streamline your freight broker operations. Click here to learn more.
Choosing the Best Insurance Providers
Finding the best freight broker insurance companies requires thorough research and comparison. Some leading companies offer specialized packages tailored to freight brokers’ needs. Consider factors like claim response time, coverage limits, and industry reputation when evaluating providers.
For instance, a study by the Transportation Intermediaries Association (TIA) found that brokers proactively manage their insurance policies and reduce financial risks by 40% (TIA, 2022).
“Selecting the right provider can significantly affect the quality of service and claim handling. It’s not just about the cost; reputation and customer support are crucial.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is contingency insurance for freight brokers?
Contingency insurance provides backup coverage for freight brokers when a carrier’s cargo insurance fails to pay for a loss. It ensures brokers are not financially responsible for damaged or lost goods due to carrier coverage gaps.
- How much is a freight broker license?
The cost of obtaining a freight broker license varies but typically includes a $300 application fee from the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), plus additional costs for surety bonds and insurance.
- How much does freight broker training cost?
Freight broker training programs range from $500 to $3,000, depending on the provider and course depth. Online programs tend to be more affordable than in-person training.
- How much is a broker license for trucking?
A trucking broker license costs $300 for the FMCSA application fee, but additional expenses, such as a $75,000 surety bond and insurance, can bring the total startup costs to around $5,000 to $10,000.
Get the Right Freight Broker Insurance
Navigating the world of freight brokerage insurance can be challenging, but understanding the costs and requirements can help brokers make informed decisions. Whether considering contingent cargo insurance for brokers, general liability, or specialized coverage, securing the right insurance plan is essential for protecting your business and maintaining compliance with industry standards. Investing in comprehensive cargo insurance for freight brokers ensures long-term success and financial security.
Ready to safeguard your Freight Business? Contact us for expert guidance on the best insurance options for long-term protection and success.
References
References
Transportation Intermediaries Association. (2022). Freight Broker Risk Management Report. Retrieved from https://www.tianet.org
American Transportation Research Institute. (n.d.). Cargo Theft Statistics. Retrieved from https://www.atri-online.org
Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration. (n.d.). Broker Licensing Requirements. Retrieved from https://www.fmcsa.dot.gov
FreightWaves. (2023). Contingent Cargo Insurance Case Study. Retrieved from https://www.freightwaves.com




