Your supply chain’s security posture can determine the success or failure of your entire operation. From data breaches to operational sabotage, modern threats demand robust cyber protection. Supply chain safety is no longer just about physical goods, it’s about digital integrity, resilience, and proactive risk management.
In this guide, we’ll break down essential strategies for securing your supply chain, explore critical cyber threats, and share supply chain security best practices every business should follow.
What Is Supply Chain Security?
Supply chain security refers to the systems, procedures, and technologies designed to safeguard the integrity of the supply chain from physical and cyber threats. It includes protecting goods in transit, ensuring supplier credibility, and mitigating digital vulnerabilities.
Example: In 2020, hackers targeted a major electronics manufacturer by breaching one of its third-party software providers. This compromise affected operations worldwide, emphasizing the need for end-to-end supply chain security (CrowdStrike, 2021).
“Supply chain security is now a boardroom priority. Organizations must recognize that their cybersecurity posture is only as strong as their most vulnerable third-party vendor.”
How confident are you in your current visibility into supplier risks across your global supply chain?
Benefits of Supply Chain Security
Implementing strong supply chain security practices delivers significant benefits:
- Reduced Risk of Disruption – Secure supply chains are more resilient to cyberattacks and physical threats.
- Enhanced Customer Trust – Clients prefer working with companies that protect their data and products.
- Regulatory Compliance – Helps meet requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and CISA directives.
- Operational Efficiency – Prevents unplanned downtime caused by ransomware or fraud.
According to IBM, companies with fully deployed security automation experience 80% lower average breach costs than those without it (IBM, 2023).
“Supply chain resilience is no longer a competitive edge, it’s a core requirement. Building security into every layer is essential for continuity and trust.”
What benefit of supply chain security has made the biggest impact on your business or industry?
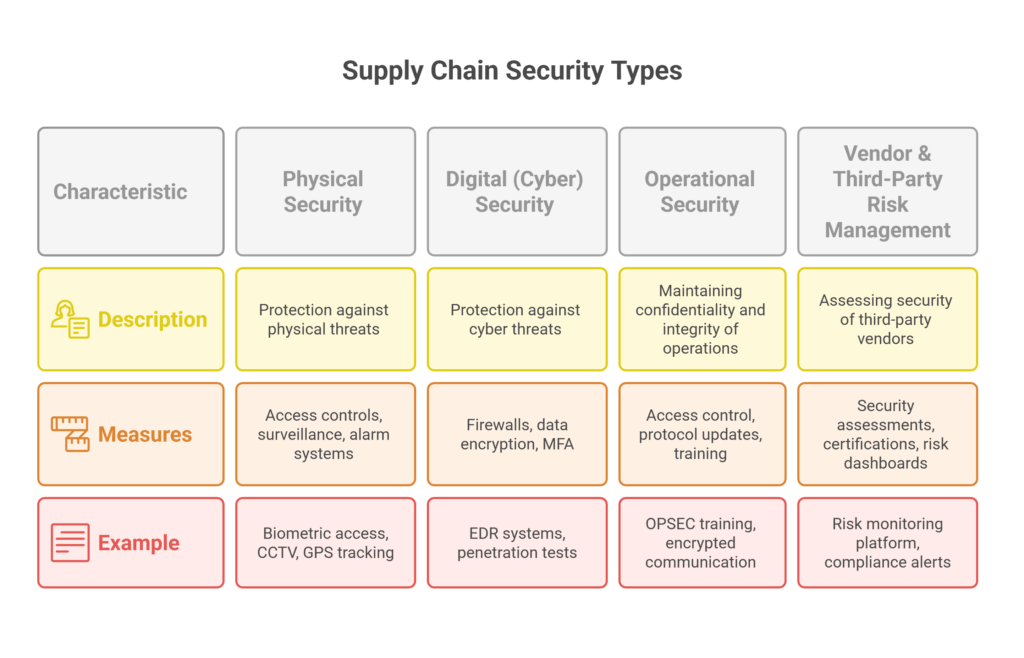
Types of Supply Chain Security
There are several categories of supply chain security that businesses must address:
1. Physical Security: is the frontline defense of any supply chain. It involves protecting facilities, transport vehicles, warehouses, and goods from physical theft, damage, or sabotage. This includes implementing access controls, surveillance cameras, alarm systems, and security personnel.
Example: A distribution center uses biometric access controls, motion-detection CCTV, and GPS-enabled trucks to prevent unauthorized entry and track cargo in real time, significantly reducing theft incidents.
2, Digital (Cyber) Security
This area involves protecting digital assets—systems, networks, and data—from cyberattacks. It includes deploying firewalls, encrypting sensitive data, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and securing IT infrastructure used across the supply chain.
Example: A logistics company integrates endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems across all connected devices and performs regular penetration tests to identify potential vulnerabilities in their transportation management system.
3. Operational Security
Operational security (OPSEC) focuses on maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of operations. This includes enforcing strict access to operational data, regularly updating protocols, and educating employees about phishing, social engineering, and secure communication.
Example: A food manufacturer implements regular OPSEC training and a strict policy requiring encrypted communication for all vendor interactions, minimizing data leaks and insider threats.
4. Vendor & Third-Party Risk Management
Because many supply chain functions are outsourced, it’s essential to assess the security posture of all third-party vendors. This includes evaluating their cybersecurity measures, requiring certifications like ISO 27001, and maintaining real-time vendor risk dashboards.
Example: A retail chain uses an automated risk monitoring platform to continuously evaluate all supplier networks, triggering alerts for any non-compliance or emerging cyber threats from partners.
“A secure supply chain blends physical protection, operational discipline, and cyber defense. Each pillar plays a vital role in minimizing disruption and maximizing uptime.”
Which type of supply chain security do you think is most often overlooked, and why?
Why Supply Chain Safety Is No Longer Optional
Gone are the days when supply chain safety meant securing warehouses and transport routes. Today, it also includes:
- Protecting digital infrastructure
- Vetting third-party vendor software
- Guarding sensitive data in transit
Supply chain safety now depends on a robust blend of physical and digital defenses, with cyber supply chain threats on the rise globally.
89% of companies have experienced a supplier-related security incident in the past 12 months (Ponemon Institute).
“Attackers increasingly target the weakest link, often a third-party vendor. Proactive safety protocols are the only way to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.”
Has your organization made supply chain safety part of executive-level risk discussions?
Top Supply Chain Security Best Practices to Implement
To improve resilience, reduce downtime, and mitigate risk, every company must adopt supply chain security best practices such as:
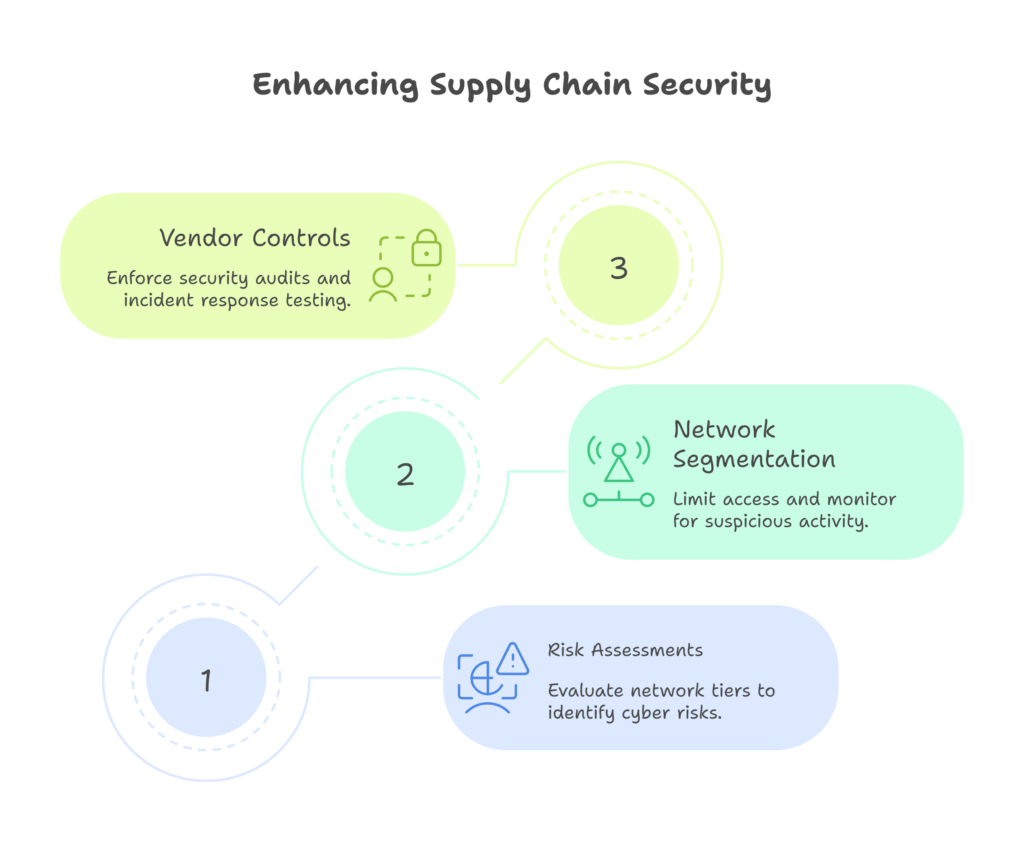
1. Conduct Thorough Cyber Supply Chain Risk Assessments
Evaluate every tier of your network, from logistics providers to cloud vendors, to identify cyber supply chain risk.
2. Segment and Monitor Networks
Limit access between different parts of your operation and install monitoring tools that flag suspicious activity across all nodes.
3. Enforce Vendor Risk Controls
- Require third-party security audits
- Include cyber clauses in contracts
- Regularly test incident response with partners
These actions are essential to cyber supply chain risk management, helping prevent external vulnerabilities from disrupting operations.
“Best practices in supply chain security aren’t static checklists, they’re evolving frameworks that must adapt to emerging threats and technologies.”
Ready to implement security strategies that make a real difference? Explore our shipping services to see how we help protect your freight every step of the way.
Key Steps to Building a Resilient Cyber Supply Chain
Step 1: Create a Supply Chain Cyber Security Framework
Use ISO, NIST, or similar standards to establish policies, assign ownership, and monitor compliance.
Step 2: Map Your Digital Supply Chain
Understand where your data flows, who touches it, and which systems interact to build cyber resilience into your supply chain cyber security strategy.
Step 3: Integrate Cyber Security in Supply Chain Management
Embed cyber protection into planning, procurement, and logistics by adopting cyber security in supply chain management principles.
Step 4: Use Predictive Analytics
Spot trends, anticipate disruptions, and make proactive decisions with predictive tools and AI-enhanced monitoring (Accenture, 2022).
Step 5: Establish Cross-Functional Cyber Risk Teams
Collaboration between IT, logistics, procurement, and legal teams ensures end-to-end protection across the cyber supply chain.
“A resilient cyber supply chain requires collaboration across business units. It’s not just about firewalls, it’s about shared responsibility from procurement to IT.”
What’s one internal process you’ve improved to increase supply chain cyber resilience?
What Is Supply Chain Cyber Risk Management?
Supply chain cyber risk management focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating cyber threats across every layer of the supply chain. This includes:
- Insider threats
- Malware and ransomware attacks
- Data integrity risks from third parties
- Intellectual property theft
You must manage both direct and inherited risks. Strong supply chain security management is the key to controlling these evolving threats.
Example: After the SolarWinds breach, many businesses were forced to reevaluate their third-party software exposure and implement stricter supplier vetting (CISA, 2021).
“Managing cyber risk in the supply chain is about managing trust. If you don’t know who has access to your data, you’re already exposed.”
Have you conducted a recent audit of cyber risk across your entire supply chain?
Common Supply Chain Security Risks You Must Know
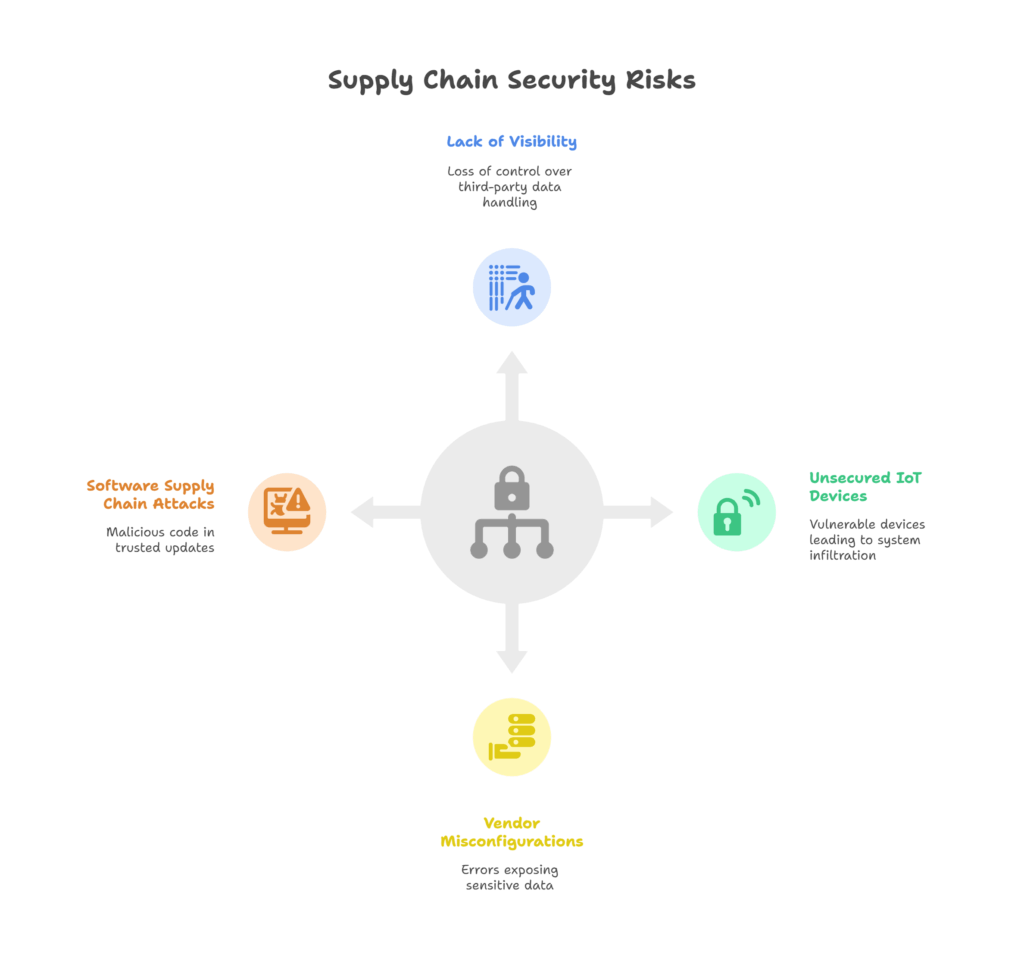
1. Lack of visibility across third-party platforms: When companies outsource services or rely on third-party vendors for critical operations, they often lose sight of how data and systems are handled outside their immediate control. This lack of transparency can conceal cyber vulnerabilities, delay breach detection, and create compliance gaps. Without real-time visibility, organizations struggle to detect anomalies or respond swiftly to threats introduced by vendors.
2. Unsecured IoT devices in logistics and inventory: Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as smart sensors, tracking beacons, and automated inventory systems have become essential to modern logistics. However, many of these devices are deployed with weak or default credentials and minimal encryption. Cybercriminals can exploit these unsecured endpoints to infiltrate broader systems, manipulate data, or even cause physical disruptions to warehouse operations.
3. Data breaches from vendor misconfigurations: Misconfigured servers, unsecured cloud platforms, and incorrect permissions are common vendor-side errors that can expose sensitive data. These breaches often occur when third-party providers overlook security hygiene, such as leaving storage buckets public or failing to encrypt data at rest. Despite being the vendor’s fault, your brand and customers could still bear the consequences.
4. Software supply chain attacks (e.g., SolarWinds): In a software supply chain attack, adversaries compromise a trusted software provider and insert malicious code into legitimate updates. The SolarWinds breach, which impacted thousands of organizations globally, is a prime example. These attacks are particularly dangerous because they exploit the inherent trust placed in software updates and can remain undetected for long periods, spreading malware across vast networks.
These are just a few examples of supply chain security risks that can cripple even well-prepared companies.
“Third-party risk is one of the fastest-growing threat vectors in cybersecurity. Most breaches start with a weak or compromised vendor.”
What’s one recent supply chain security risk you’ve addressed, and what was your solution?
How to Reduce Supply Chain Security Issues
To address these risks, businesses must:
- Incorporate supply chain cyber risk into enterprise risk models
- Perform routine audits
- Train employees on security awareness
- Invest in endpoint and network protection
- Update third-party risk governance models
Addressing supply chain security issues early helps maintain business continuity and reputation.
By 2026, 70% of organizations will increase investments in third-party risk management tools (Gartner, 2023).
Supply chain security risk management is no longer an IT-only function. Today, it involves every part of an organization, from legal to procurement. A holistic approach involves:
- Threat intelligence sharing with partners
- Cyber insurance for operational risk
- Integrating cyber supply chain risk into disaster recovery plans
- Promoting cross-sector collaboration
These techniques reduce your supply chain risk cyber security exposure and build long-term resilience.
“Supply chain security must evolve from technical control to enterprise-wide governance. True resilience comes from shared accountability across every department.”
Want to proactively reduce your risk exposure? Explore our compliance and risk management solutions tailored to modern supply chain needs.
Real-World Consequences of Ignoring Supply Chain Security
Companies that overlook supply chain cyber security often face:
- Regulatory fines
- Reputational damage
- Product recalls or delays
- Customer trust erosion
Modern cyberattacks exploit weak links quickly. A single breach can affect dozens of partners across your cyber supply chain.
“Ignoring supply chain security is like driving without insurance, risky, short-sighted, and potentially catastrophic for brand trust and continuity.”
Curious how to protect your brand and partners from real-world security failures? Discover freight broker solutions that prioritize safety and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the best supply chain security best practices for reducing cyber threats?
Effective supply chain security best practices include conducting regular vendor audits, encrypting data at every stage, using multi-factor authentication, and implementing endpoint protection. These steps not only enhance your supply chain safety but also lower the risk of breaches across your network.
2. How can I manage cyber supply chain risks across multiple vendors?
To manage cyber supply chain risk, start by mapping out all third-party access points and assessing each vendor’s cybersecurity protocols. Use frameworks like NIST or ISO 28000 for structured supply chain cyber risk management. Automated risk scoring tools can help you track vulnerabilities and prioritize mitigation efforts.
3. Why is cyber security in supply chain management a growing concern in 2025?
With the rise of interconnected systems and cloud-based logistics, cyber security in supply chain management is more critical than ever. A single exposed endpoint or compromised vendor can trigger a massive operational breakdown, making supply chain cyber security a board-level priority for modern organizations.
Secure Your Supply Chain
Cyber threats aren’t going away, they’re evolving. By implementing supply chain security best practices, investing in cyber supply chain risk management, and prioritizing safety across every touchpoint, your organization can stay ahead of attackers and thrive in today’s digital-first economy.
Ready to strengthen your supply chain security? Contact us to build a safer, smarter logistics strategy.
References
Accenture. (2022). The supply chain of the future. Retrieved from Discover more
CISA. (2021). SolarWinds and supply chain attacks. Retrieved from Discover more
CrowdStrike. (2021). Global supply chain attacks report. Retrieved from Discover more
Gartner. (2023). Future of third-party risk management. Retrieved from Discover more
IBM. (2023). Cost of a data breach report. Retrieved from Discover more
Ponemon Institute. (2023). State of supply chain security. Retrieved from Discover more




