Independent brokers are no longer small targets, they’re high-value gateways into shipper data, carrier payment flows, and supply chain operations. As digital freight tools expand and fraud rings grow more sophisticated, freight broker cybersecurity has become a business survival issue, not just an IT concern.
This guide breaks down the most common and high-impact cybersecurity threats for freight brokers, explains how attacks actually happen, and shows how to prevent cyber attacks in freight brokerage using practical, field-tested safeguards.
Why Freight Brokers Are Prime Cyber Targets
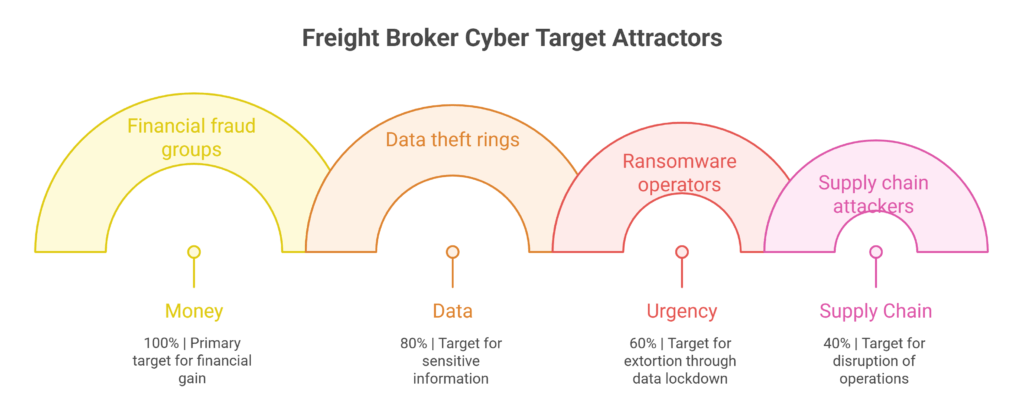
Freight brokers sit at the intersection of money, data, and operational urgency, the perfect storm for attackers exploiting cybersecurity risks in logistics industry environments (Transportation Intermediaries Association [TIA], 2024).
Brokers typically manage:
- Carrier onboarding & payment details
- Rate confirmations & load tenders
- Banking transactions and quick-pay requests
- Access to TMS, load boards, and email systems
That combination attracts:
- Financial fraud groups
- Data theft rings
- Ransomware operators
- Supply chain attackers
And unfortunately, most independent firms still lack structured small logistics company cyber protection strategies.
“Even small security lapses can cost brokers big because they handle money and sensitive data daily.”
Which area of your brokerage is most at risk if hacked;payments, carriers, or shipper data?
The Most Common Cybersecurity Threats for Freight Brokers
1. Phishing & Identity Takeover
One of the fastest-growing threats is phishing scams targeting freight brokers. Attackers impersonate:
- Legitimate carriers
- Factoring companies
- Internal staff
- Load board messages
- Shippers requesting urgent updates
Why it works
Freight runs at speed. Brokers react fast and fraudsters exploit that urgency.
Impact
- Carrier identity hijacking
- Load theft
- Payment redirection
- System compromise
Phishing is now the top entry point behind most data breaches in freight companies (IBM Security, 2024).
“Freight phishing is social engineering disguised as operations. Brokers who verify carrier identity like banks verify customers reduce theft dramatically.”
Would your current carrier onboarding process catch a stolen identity using a real MC and insurance file?
2. Wire & Payment Fraud
The wire transfer fraud logistics industry problem is exploding. Criminals infiltrate email threads and quietly change:
- ACH instructions
- Carrier payment accounts
- Factoring destinations
Common scenario
- Hacker gains email access
- Watches payment conversations
- Sends “updated banking” request
- Broker unknowingly wires funds
Losses are often unrecoverable and devastating for independent brokerages (IBM Security, 2024).
“If payment verification isn’t a formal step, it’s an open door. Cybercriminals treat broker emails like financial control panels.”
How many payment destinations can currently be changed inside your brokerage without secondary approval?
3. Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks in transportation are hitting logistics harder every year, with increasing logistics company ransomware cases reported across brokerages and carriers.
What happens
- Files encrypted
- TMS locked
- Customer data frozen
- Operations halted
Recent cyber attacks in supply chain reports show freight intermediaries are among the top victims because attackers know downtime equals panic payments (FBI Internet Crime Report, 2024).
“Ransomware attackers don’t target systems, they target operational panic. Brokers pay because freight cannot stop.”
If your TMS was frozen today, how long before your customers move their freight elsewhere?
4. Malware Infiltration
Malware attacks on trucking companies often spread to brokers through shared documents, fake rate sheets, or infected email attachments (CISA, 2025).
Malware allows criminals to:
- Record keystrokes
- Steal credentials
- Control devices remotely
- Monitor financial activity
This is a major weakness in broker environments lacking hardened freight broker cybersecurity defenses.
“Every freight attachment is a potential doorway. Cybercriminals weaponize trust in routine documents.”
Do you or your staff open freight attachments without verifying sender authenticity?
5. Data Breaches & System Intrusions
Brokers hold extremely monetizable logistics data.
What hackers target
- Carrier payment lists
- Shipper lane pricing
- Contracted rates
- Insurance documents
- Email archives
How breaches occur
- Weak passwords
- No MFA
- Cloud misconfigurations
- Malware backdoors
Why this is dangerous
Stolen data fuels:
- Future phishing
- Fake carrier setups
- Competitive exploitation
- Financial fraud loop
“Stolen data becomes future theft. Every breach multiplies risk across carriers and shippers.”
If your carrier database leaked, how many fake identities could criminals build from it?
6. Supply Chain Platform Exploits
Freight tech stacks are deeply interconnected:
- Load boards
- TMS platforms
- Carrier vetting tools
- Accounting software
Weak vendor security creates entry paths for broad cyber attacks in supply chain events (Gartner Supply Chain Security Report, 2025).

“You’re only as secure as the weakest tech platform connected to your brokerage.”
Concerned about hidden vulnerabilities in your freight tech stack? Protect your brokerage with secure, scalable solutions here.
How to Prevent Cyber Attacks in Freight Brokerage
Cybersecurity in brokerage isn’t about expensive tools, it’s about closing the exact gaps criminals exploit. Most freight broker cyber incidents come from predictable weaknesses in identity verification, payment workflows, system access, and staff awareness.
Below is a thorough, freight-specific prevention strategy built around real brokerage operations.
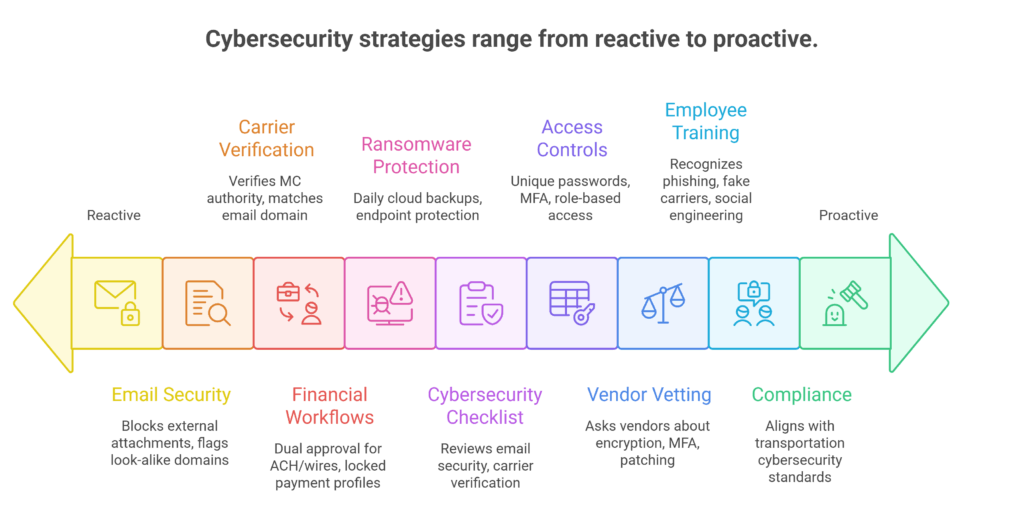
1. Lock Down Email
Email is the main gateway for:
- Phishing scams targeting freight brokers
- Wire transfer fraud logistics industry schemes
- Carrier identity hijacking
- Malware infiltration
Action Steps
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) on ALL email accounts
- Use domain protection (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
- Block external attachments with executable content
- Flag look-alike domains automatically
- Train staff to never trust banking or carrier changes via email alone
Without email protection, freight broker cybersecurity collapses at the entry point (TIA, 2024).
2. Enforce Carrier Identity Verification Protocols
Most cyber-enabled freight theft starts with fake carriers.
Build this process into operations:
- Verify MC authority age & activity
- Match carrier email domain to FMCSA records
- Require direct phone verification (not numbers in email)
- Validate insurance directly with provider
-
Watch for red flags:
- Gmail-only carriers
- Recently reactivated MCs
- Dispatch urgency pressure
This is one of the most overlooked freight broker IT security best practices.
3. Secure Financial Workflows to Stop Payment Fraud
Wire transfer fraud logistics industry losses are growing because brokers rely on email-based approvals.
Mandatory Safeguards
- Dual approval for ACH/wires
- Locked carrier payment profiles
- Call-back verification for ANY banking change
- Payment freeze for new accounts
- Separate accounting login from operations
These steps alone prevent the majority of broker financial cybercrime.
4. Protect Systems Against Ransomware
Ransomware attacks in transportation target small brokers with weak IT environments (TIA, 2024).
Prevention Framework
- Daily cloud backups (isolated from network)
- Endpoint protection on every device
- Disable open remote desktop ports
- Limit admin privileges
- Patch TMS and accounting software weekly
Many logistics company ransomware cases happened because backups were connected and encrypted too.
5. Use a Cybersecurity Checklist for Freight Brokers
A working cybersecurity checklist for freight brokers should be reviewed quarterly.
Core Checklist Areas
- Email security
- Carrier verification workflow
- Banking protection process
- Vendor access control
- Password policy enforcement
- Backup validation
- Staff cyber training
Following a structured cybersecurity checklist for freight brokers ensures nothing critical is left exposed.
6. Limit Access & Strengthen Password Controls
Weak credentials cause most data breaches in freight companies.
Best Practices
- Unique passwords for every system
- MFA across TMS, load boards, banking
- Role-based access limits
- Remove former employee access immediately
- Use password managers
Simple access discipline dramatically improves small logistics company cyber protection (FMCSA Cyber Guidance, 2025).
7. Vet Your Technology Vendors
Freight platforms are a growing risk in cyber attacks in supply chain 2026.
Ask vendors:
- Do you use encryption?
- Do you require an MFA?
- How often are systems patched?
- What happens in a breach?
Weak vendors create hidden freight broker cybersecurity exposure.
8. Train Employees Like a Security Team
Your staff is your frontline defense.
Train them to recognize:
- Phishing scams targeting freight brokers
- Fake carrier packets
- Urgent payment manipulation
- Suspicious attachments
- Social engineering calls
Human awareness prevents more attacks than software.
9. Follow Transportation Cybersecurity Compliance
Compliance isn’t optional anymore.
Align with transportation cybersecurity compliance standards to:
- Protect shipper contracts
- Reduce legal risk
- Meet insurance requirements
- Avoid penalties after breaches
Regulators are paying closer attention after repeated ransomware attacks in transportation.
“Cybercriminals don’t hack freight brokers, they exploit rushed decisions and skipped verification.”
Ready to strengthen your brokerage with safer, smarter freight technology? Explore our freight broker technology to see advanced protection tools designed for brokers
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why are independent freight brokers heavily targeted by cybercriminals?
Because brokers control payments, carrier onboarding, and shipper data — making them high-value entry points within cybersecurity risks in logistics industry networks.
2. What is the most common cyberattack against freight brokers?
Phishing scams targeting freight brokers are the leading cause of fraud, load theft, and financial compromise.
3. How can a small brokerage realistically improve cybersecurity?
By applying freight broker IT security best practices, using a cybersecurity checklist for freight brokers, enforcing payment verification, and adopting small logistics company cyber protection tools.
Protect Your Brokerage Before It’s Targeted
Cyber threats are now operational threats. From phishing and wire fraud to ransomware and malware, today’s cybersecurity threats for freight brokers can wipe out revenue, reputation, and customer trust overnight.
Independent brokers who implement structured freight broker IT security best practices, follow a complete cybersecurity checklist for freight brokers, and actively invest in small logistics company cyber protection will not only reduce risk, they’ll gain a competitive edge in an increasingly vulnerable logistics landscape.
Want to strengthen your freight brokerage against cyber risks before they cost you a shipment or a client? Contact our team and let’s secure your operations.
References
Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). (2025). Cyber threats to the transportation sector. Retrieved from https://www.cisa.gov
Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). (2025). Transportation cybersecurity compliance guidance. Retrieved from https://www.fmcsa.dot.gov
Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). (2024). Internet Crime Report – Business Email Compromise. Retrieved from https://www.ic3.gov
Gartner. (2025). Supply chain cybersecurity risks report. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com
IBM Security. (2024). Cost of data breaches in logistics. Retrieved from https://www.ibm.com/security
Transportation Intermediaries Association (TIA). (2024). State of freight broker cybersecurity. Retrieved from https://www.tianet.org




