If you’ve ever wondered how freight brokers fit into the supply chain, and more importantly, how they earn their income, this blog is your guide. Freight brokers are vital in the logistics industry, serving as the middlemen between shippers and carriers. Their earnings can vary, but understanding freight broker commission structures, typical freight broker rates, and how much brokers make per load is key to grasping their business model.
What is Freight Broker Commission?
Freight broker commission refers to the earnings a freight broker makes by arranging transportation services between shippers and carriers. This commission is the broker’s cut from the total payment made by the shipper after paying the carrier.
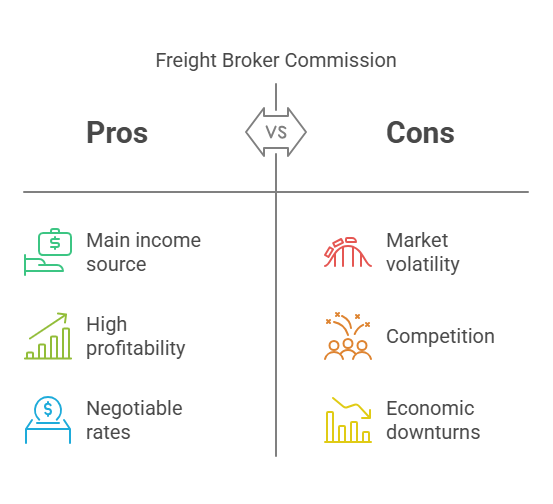
- A well-negotiated freight broker commission can lead to high profitability (FreightWaves, 2024).
- It is the main source of income for freight brokers.
- Derived from the difference between what the shipper pays and what the carrier receives.
- Also called the “margin” or “spread.”
“A clear understanding of freight broker commission helps new brokers price effectively and remain competitive in changing markets.”
How Do Freight Brokers Get Paid?
A freight broker doesn’t own trucks or cargo. Instead, they coordinate shipments between those who need freight moved and the carriers who have the capacity to move it. So, how do freight brokers get paid? They typically charge the shipper a higher rate than they pay the carrier, and the difference is their profit, commonly referred to as the freight broker commission.
- The earnings model is scalable based on load volume.
- Freight broker commission is included in the total rate charged to the shipper.
- Payment is usually collected upfront or after successful delivery.
- Technology platforms often facilitate instant quoting and payment processes (Freightos, 2024).
“Leveraging digital platforms and automation tools can accelerate payment cycles and help brokers manage commissions more effectively.”
What are some pros and cons of relying entirely on commission-based income as a freight broker?
Commission Models for Freight Brokers
There are several commission models used in the freight brokerage industry. The choice depends on the business structure, partnerships, and market focus.
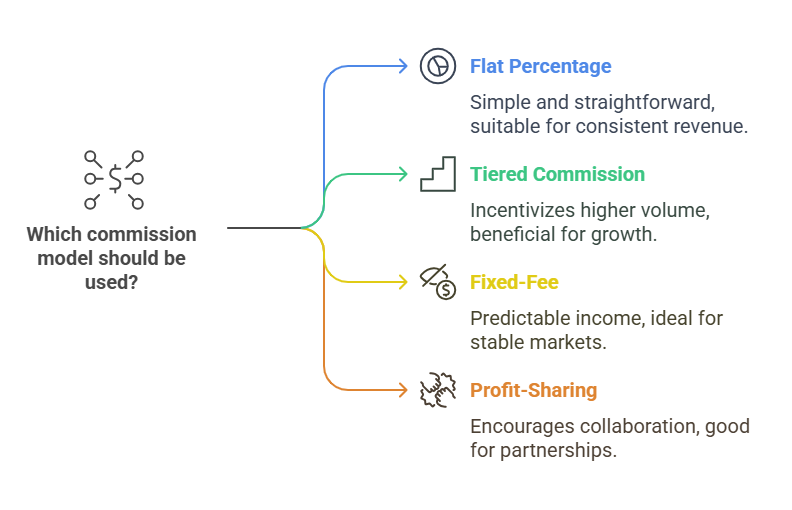
1. Flat Percentage Commission: Brokers earn a fixed percentage (e.g., 15%) of the total shipment cost.
For example, if a broker arranges a $2,000 shipment and takes a 15% freight broker commission, they would earn $300 regardless of other factors. This model provides consistent income per shipment (FreightWaves, 2024).
2. Tiered Commission: Commission percentage increases with higher volume or revenue thresholds.
For example, a brokerage firm might offer 10% commission for up to $50,000 in monthly revenue, and 20% once the broker surpasses that threshold. This model rewards high-performing brokers with greater income potential.
3. Fixed-Fee Model: A set dollar amount per load, regardless of shipment value.
For example, a broker may earn $150 per load whether the shipment costs $1,000 or $3,000. This model works well in standardized markets where pricing is predictable, but may limit profit on high-value loads.
4. Profit-Sharing: Brokers and agents split the net profit from each load based on predefined terms.
For example, if the total profit on a load is $500 after paying the carrier, the broker might keep 60% ($300), and the agent receives 40% ($200). This model encourages collaboration and shared responsibility for margin management.
Each model impacts how much a freight broker makes per load and overall profitability depending on how loads are sourced, priced, and managed.
“Choosing the right commission model depends on broker experience, business volume, and niche specialization, new brokers may benefit from flat-rate models to maintain steady income.”
Which commission model do you think offers the best balance between stability and earnings potential for new brokers?
Freight Broker Commission Percentage Explained
A common question in the industry is: what is the average freight broker commission percentage? Typically, it ranges between 10% and 35%, depending on the complexity of the shipment, the route, the type of cargo, and market conditions (Indeed, 2024).
1. Independent Freight Brokers: These brokers work for themselves and typically retain the full commission from each load they arrange.
For example, if an independent broker negotiates a 25% freight broker commission on a $2,500 load, they take home the full $625. While they bear the full responsibility for finding clients, managing loads, and ensuring smooth transactions, they also enjoy the full financial reward. This model offers high income potential, especially for experienced brokers with strong industry networks and negotiation skills.
2. Employed Freight Brokers: These brokers work under a brokerage firm or logistics company. They usually receive a fixed salary or a percentage split of the freight broker commission earned per load.
For instance, if the company earns a 25% commission on a $2,500 load ($625), the broker may receive 50% of that amount, equaling $312.50. While their income per load is lower, employed brokers benefit from company support, lead generation, technology platforms, and back-office assistance, which can offer more job security and a consistent workflow.
Freight broker rates are also influenced by how much time and negotiation is required to secure reliable carriers. A broker who provides high-quality service and has strong industry connections can often command a better commission structure.
- Market trends heavily influence the average freight broker commission percentage. For instance, during peak seasons or in volatile fuel markets, commission percentages may either rise due to urgency or drop due to tightened margins.
- 15–25% is a common range in most standard freight lanes. For example, a broker managing regular routes for retail goods might consistently earn a 20% commission on shipments valued at $2,000, resulting in a $400 commission per load.
- Niche or expedited loads may allow for commissions of up to 35%. A broker specializing in urgent medical supply shipments may charge a premium due to time sensitivity and complexity, earning $700 on a $2,000 load.
- Lower commissions (10–15%) are typical for high-volume contracts. Employed brokers working with major logistics firms may handle 20+ loads daily with a smaller margin, such as 12% on each $1,500 shipment, generating about $180 per load, but with high frequency.
“A broker’s ability to provide added value, such as faster booking times or better carrier vetting, can justify a higher commission percentage in competitive markets.”
Looking for a more detailed breakdown of freight broker earnings and percentages? Learn more here.
How Much Does a Freight Broker Make Per Load?
When it comes to income, you might be asking: how much does a freight broker make per load? This varies significantly. For instance, on a $1,500 shipment, if a broker takes a 20% freight broker commission percentage, they earn $300.
- Earnings per load range from $100 to $500+.
- Specialized or expedited freight may offer higher earnings.
- Brokers working independently may retain full commission, while those at firms may split it.
- Load complexity and negotiation skills affect commission size.
So, how much do freight brokers make per load consistently? It depends on volume, specialization, and market demand. Some brokers handle dozens of loads per week, while others focus on high-value, specialized shipments.
“The key to higher earnings per load lies in securing niche lanes and leveraging long-term shipper-carrier partnerships.”
What strategies can brokers use to consistently increase their earnings per load, especially in competitive or low-margin freight lanes?
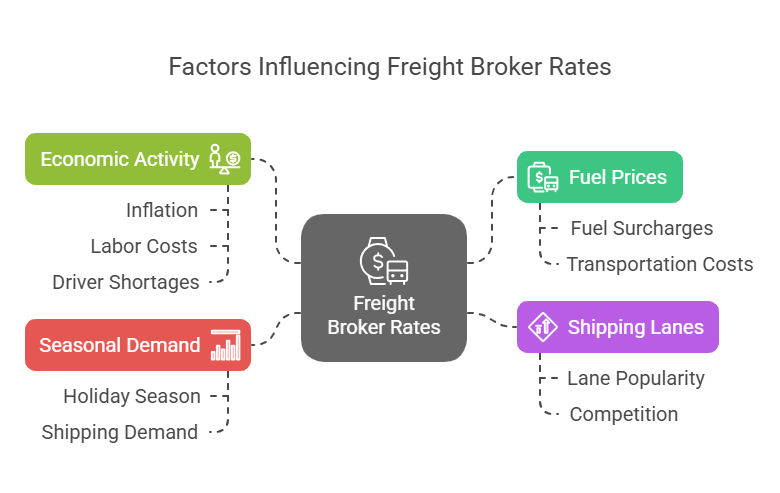
Factors That Influence Freight Broker Rates
Freight broker rates aren’t static, they’re influenced by fuel prices, shipping lanes, seasonal demand, and overall economic activity. For instance, freight broker rates typically rise during the holiday season when shipping demand spikes (DAT Freight & Analytics, 2024).
- Lane popularity: Higher competition can lower rates.
For example, a broker arranging freight on a popular lane like Los Angeles to Dallas may face lower margins due to multiple carriers competing for loads, reducing the broker’s ability to mark up rates significantly.
- Distance and delivery time: Long-hauls and tight deadlines often increase rates.
For example, a shipment from New York to Seattle with a 48-hour deadline may allow a broker to negotiate a premium, increasing the freight broker commission due to the urgency and fuel costs involved.
- Freight type: Perishables or hazardous materials command higher margins.
For instance, a load of frozen seafood requiring refrigerated transport may have a higher commission potential because fewer carriers offer this service, allowing brokers to charge a premium.
- Economic conditions: Inflation, fuel surcharges, and labor costs all play a role. During periods of high fuel prices or driver shortages, brokers can often justify higher rates to shippers, increasing their profit margin per load.
For example, during the 2021 fuel surge, brokers handling long-haul routes saw their freight broker rates increase by 10-15%.
- Negotiation: freight broker’s ability to negotiate with both shippers and carriers. Those with advanced technology and data-driven insights can often optimize routes and pricing, improving their commission and profitability.Check out our blog to understand how to connect with shippers as a freight broker
For example, a tech-savvy broker using real-time freight analytics might identify backhaul opportunities that maximize truck usage, reducing costs for the carrier and increasing margins for the broker.
“Smart brokers use data analytics and market visibility tools to capture better rates, reduce deadhead miles, and build stronger lanes.”
Curious about smart pricing strategies and margin-boosting insights? Explore our Freight Broker Solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQS)
1. How much does a freight broker make per load?
Freight brokers typically earn $100 to $500+ per load, depending on the load value and freight broker commission percentage.
2. What is the average freight broker commission percentage?
The typical freight broker commission percentage ranges from 10% to 35%, based on shipment type, urgency, and market demand.
3. How do freight broker rates impact earnings?
Higher freight broker rates lead to greater profits per load, especially in niches like refrigerated freight or expedited shipping.
Claim Your Freight Broker Commission
Understanding freight broker commission, how brokers get paid, and the typical freight broker commission percentage is essential for anyone entering the logistics world. Knowing how much a freight broker makes per load or the typical freight broker rates can help shippers and new brokers alike set realistic expectations.
Ready to take control of your freight profits? Contact us to discover how successful agents grow.
References
DAT Freight & Analytics. (2024). Freight Broker Market Trends. Retrieved from https://www.dat.com
FreightWaves. (2024). Freight Broker Earnings and Industry Insights. Retrieved from https://www.freightwaves.com
Freightos. (2024). How Freight Brokers Get Paid. Retrieved from https://www.freightos.com
Indeed. (2024). Freight Broker Salary Guide. Retrieved from https://www.indeed.com




