Rail freight shipping is a pivotal component of the global logistics network, offering a sustainable, cost-effective, and efficient method for transporting goods across vast distances. Whether you’re a logistics manager or a business owner, understanding how to ship rail can unlock new efficiencies and boost profitability.
What is Rail Freight?
Rail freight shipping involves the movement of goods via trains across extensive rail networks. Often confused with passenger rail services, rail freight shipping is entirely focused on transporting commodities and commercial cargo.
Key Components:
- Freight Train Containers: Standardized containers that facilitate easy loading, unloading, and transfer between different transportation modes.
- Intermodal Transport: The seamless integration of rail with other transport modes, allowing for efficient door-to-door delivery.
- Bulk Cargo: Transportation of unpackaged goods like coal, grains, and minerals in large quantities.
- Rail freight transport includes a variety of train types, from flatcars to tankers. In 2023, the U.S. freight rail system moved over 28 billion ton-miles of goods daily (Association of American Railroads [AAR], 2023).
“Rail freight provides the backbone of bulk logistics—its scalability and reach are unmatched in long-haul transport”
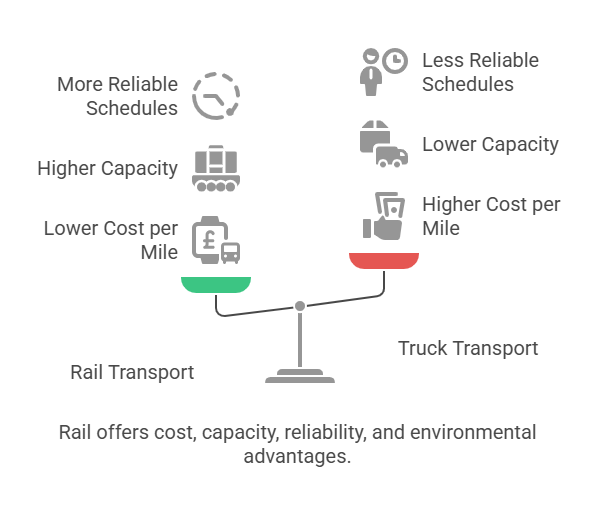
Key Benefits of Shipping by Rail
Businesses choose shipping by rail for several strategic reasons:
1. Cost Savings:
- If you’re wondering how much does it cost to ship by rail, the answer is often less than trucking for bulk loads (U.S. Department of Energy, 2022)
- Trains use less fuel per ton-mile, providing economical long-haul transport.
2. Capacity and Flexibility:
- Freight train containers allow efficient cargo movement.
- Shipping container on train systems are ideal for intermodal logistics. One double-stack train can carry the equivalent of 280 truckloads (Federal Railroad Administration [FRA], 2023).
3. Reliability:
- Railroad deliveryand railroad shipping follow consistent schedules.
- Fewer delays compared to road transport.
4. Environmental Benefits:
- Lower carbon emissions. Rail freight emits 75% fewer greenhouse gases compared to trucks for the same load (Environmental Protection Agency [EPA], 2023).
- Sustainable for companies focused on green logistics.
“Companies adopting rail logistics report lower carbon emissions and reduced fuel volatility risks”
How can businesses strategically shift to rail freight to reduce long-term shipping costs and carbon emissions without disrupting their existing supply chains?
The Mechanics of Shipping Freight by Rail
Understanding how freight train shipping works can help businesses optimize their operations:
1. Freight Train Containers:
- Standardized containers used in intermodal transport.
- Allow easy transfer between ships, trucks, and trains.
2. Shipping Container on Train:
- Ensures quicker loading and unloading.
- Reduces handling costs and cargo damage.
3. Freight Train Shipping Infrastructure:
- Includes terminals, rail yards, and connections to ports and highways.
- Supports seamless railroad delivery.
4. Freight train cargo
- Securely loaded into specialized cars based on the type of goods being transported.
Shipping freight by rail accommodates a wide range of cargo. Here’s a breakdown of common goods transported by rail
- Bulk Commodities: Coal, iron ore, grains, and other raw materials.
- Consumer Goods: Electronics, clothing, and packaged foods transported in containers.
- Automobiles: Vehicles shipped using specialized rail cars.
- Chemicals and Petroleum: Transported in tank cars designed for hazardous materials.
- Other items include: Agricultural products, Construction materials, Industrial chemicals
“Intermodal rail strategies are not just scalable, they’re future-proof, especially in a market battling fuel price hikes and labor shortages”
What are the critical operational challenges when integrating intermodal rail freight into a traditional road-based logistics network?
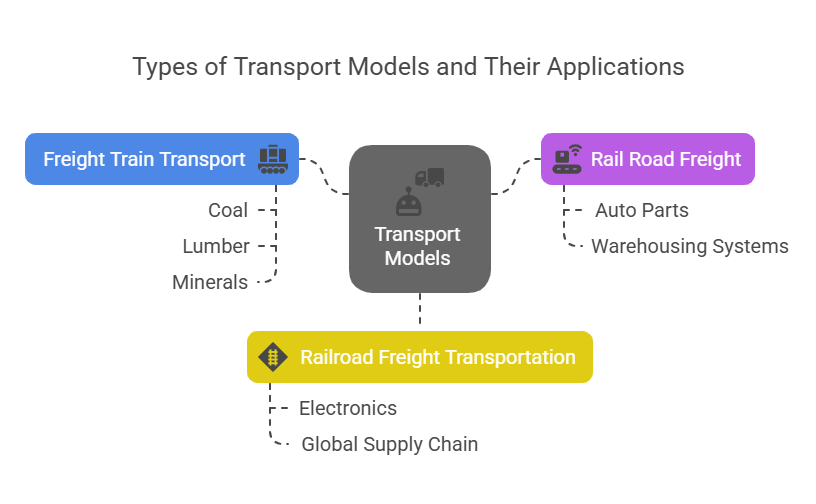
Types of transport models
Rail freight offers several models of transportation, each tailored to meet specific industry needs. These transport models are designed to enhance logistics efficiency and reduce costs through strategic planning and technological integration.
1. Freight train transport: This model is ideal for heavy bulk commodities such as coal, lumber, and minerals.
For instance, companies in the mining industry rely on this model to transport raw materials to processing plants across long distances (Mining.com, 2023)
2. Rail road freight: A hybrid solution that merges traditional rail networks with contemporary logistics technology.
For example, a manufacturer might use rail road freight to move auto parts from an inland factory to a coastal export terminal, syncing train schedules with warehousing systems for minimal downtime.
3. Railroad freight transportation: This model integrates rail, road, and maritime shipping.
For example, a global distributor may use railroad freight transportation to send electronics from a Chinese port to a European hub via a combination of train and sea, streamlining global supply chain operations (World Bank Logistics Report, 2023).
“Rail’s unmatched energy efficiency makes it the most climate-resilient option for moving freight today”
Looking for a reliable and efficient shipping solution? Learn more about our shipping services and get started.
Models and Options for Rail Shipping
Choosing the right method to ship by rail depends on your cargo and timelines:
Ship by railroad: Use large rail lines for consistent, national freight movement.
For example, national retailers often rely on this method to replenish inventory across states using well-established freight routes (AAR, 2023).
- Ship rail: Great for cross-country or intermodal needs.
For example, a logistics company moving goods from Los Angeles to New York might use ship rail to connect with ports and road freight in a seamless transition.
- Moving by rail: Ideal for long-distance relocation of commercial goods.
For example, a furniture manufacturer may relocate its products from Midwest warehouses to East Coast outlets using rail to minimize road congestion and reduce costs.
- Train shipping: Often used for cars and large machinery.
For example, automotive manufacturers frequently depend on train shipping to deliver new vehicles from assembly plants to dealerships across the country.
More options:
- Rail shipping services tailored to specific industries.
For example, agriculture-focused carriers offer rail shipping solutions that include climate-controlled cars for perishables like produce or dairy.
- Railroad delivery ensures last-mile efficiency when paired with trucking.
For example, a beverage company might use rail for bulk delivery to regional hubs, then finish the route with trucks for local store distribution.
- Railroad shipping providers offer custom schedules and tracking tools. Technology companies often choose railroad shipping for high-volume, non-urgent components that benefit from predictable delivery and real-time logistics data.
“Rail is no longer just a traditional option—it’s a strategic advantage in modern freight planning”
How can companies decide between dedicated rail shipping models and intermodal options based on cargo type, geography, and urgency?
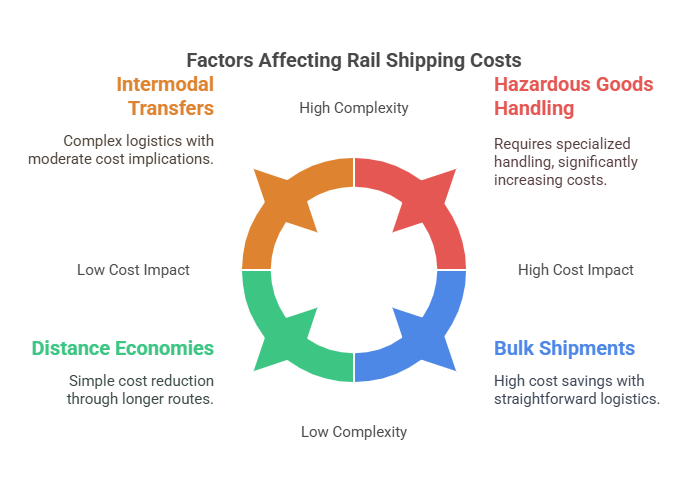
Factors affecting the cost of shipping by rail
When evaluating the cost of shipping by rail, several factors come into play:
1. Distance: Longer distances often result in lower costs per unit due to economies of scale.
Example: Shipping a container from Chicago to Los Angeles may cost less per mile compared to a shorter haul from Chicago to St. Louis due to better efficiency over longer routes.
2. Volume: Larger shipments can reduce the cost per unit.
Example: A company shipping 100 tons of coal in one bulk shipment will pay less per ton than if it were shipped in smaller, separate loads.
3. Type of Goods: Hazardous or perishable goods may incur additional costs due to special handling requirements.
Example: Shipping flammable chemicals requires specialized tank cars and compliance with safety regulations, which can increase the overall cost.
4. Route and Infrastructure: Availability of direct rail lines and the need for intermodal transfers can affect pricing.
Example: A shipment traveling along a major rail corridor with minimal transfers (e.g., from New York to Atlanta) will likely be cheaper than a shipment requiring truck-to-rail transfers in remote areas.
“While rail freight is generally more cost-effective for bulk shipping, businesses must consider route availability and specialized handling fees to get an accurate picture of total costs.”
Looking for accurate shipping quotes or a seamless carrier payment solution? Reach out to get started!
Practical Tips for Businesses
To get the most from shipping freight by rail:
- Choose freight train containers suited for your products.
- Compare costs for ship by railroad vs trucking.
- Track fuel and time savings with shipping by train metrics.
- Plan logistics with intermodal hubs that support shipping container on train infrastructure.
- Optimize your supply chain by integrating rail shipping with inventory management.
“Businesses that embed rail into their logistics DNA gain long-term cost and carbon advantages”
Looking to get started with rail freight logistics? Connect with us to discover the future of freight train cargo.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQS)
- What do freight trains carry?
Freight trains carry a wide range of goods, from agricultural products like grains and livestock to industrial materials such as steel and coal. Trains are also used to transport consumer goods, vehicles, and even hazardous materials when appropriate.
- What do railroads transport?
Railroads transport nearly every type of freight, from raw materials to finished goods. They are particularly essential for bulk shipments, including petroleum, grains, and chemicals. In addition, rail freight shipping allows for the transportation of large machinery and other heavy items.
- What is railway freight?
Railway freight is the transportation of goods via a network of railroads. This method is often preferred for long distances and large volumes of freight because of its cost efficiency and reduced environmental impact compared to other modes of transport.
- How much does it cost to ship by rail?
The cost of shipping by rail depends on various factors, including the type of goods, distance, and volume. However, rail freight generally offers more affordable pricing for large shipments than trucking, especially over long distances. On average, rail freight shipping can be 2 to 4 times more fuel-efficient than truck transport.
- What do trains transport?
Trains transport a variety of goods across vast distances, including bulk commodities like coal and minerals, consumer goods, agricultural products, and hazardous materials. The wide capacity of freight trains makes them ideal for transporting large quantities of goods efficiently.
- What are freight train containers?
Freight train containers are large, standardized containers that are used to transport goods via rail. These containers are often used in rail shipping for intermodal transport, allowing goods to be easily transferred between rail, road, and sea transport systems.
- What is freight train cargo?
Freight train cargo refers to the goods being transported on freight trains. This cargo can vary greatly, from agricultural products and machinery to fuel and construction materials. The ability of freight trains to carry large quantities makes them ideal for heavy and bulk shipments.
- How does railroad freight transportation work?
Railroad freight transportation works by utilizing specialized railcars designed for different types of cargo, including flatcars, tankers, and boxcars. Goods are loaded into these railcars and transported across long distances, with minimal environmental impact compared to trucks.
Discover the Benefits of Freight Train Shipping
Freight train shipping offers unmatched efficiency, capacity, and environmental benefits. Whether you’re transporting heavy machinery, fresh produce, or raw materials, choosing to ship by rail can transform your logistics strategy. As more companies tap into the cost savings and reliability of rail freight, it’s clear that rail is becoming the backbone of global commerce. With evolving infrastructure and advancing technology, now is the perfect time to take advantage of the momentum in rail shipping.
Ready for a smarter, more sustainable shipping solution? Contact us to explore rail freight options
References
Association of American Railroads. (2023). Freight rail facts & figures. Retrieved from https://www.aar.org
Environmental Protection Agency. (2023). Greenhouse gas emissions from transportation. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov
Federal Railroad Administration. (2023). Intermodal freight transportation overview. Retrieved from https://railroads.dot.gov
U.S. Department of Energy. (2022). Transportation energy data book. Retrieved from https://www.energy.gov
Mining.com. (2023). Global mineral freight transportation trends. Retrieved from https://www.mining.com
World Bank. (2023). Logistics performance index and global freight outlook. Retrieved from https://www.worldbank.org




